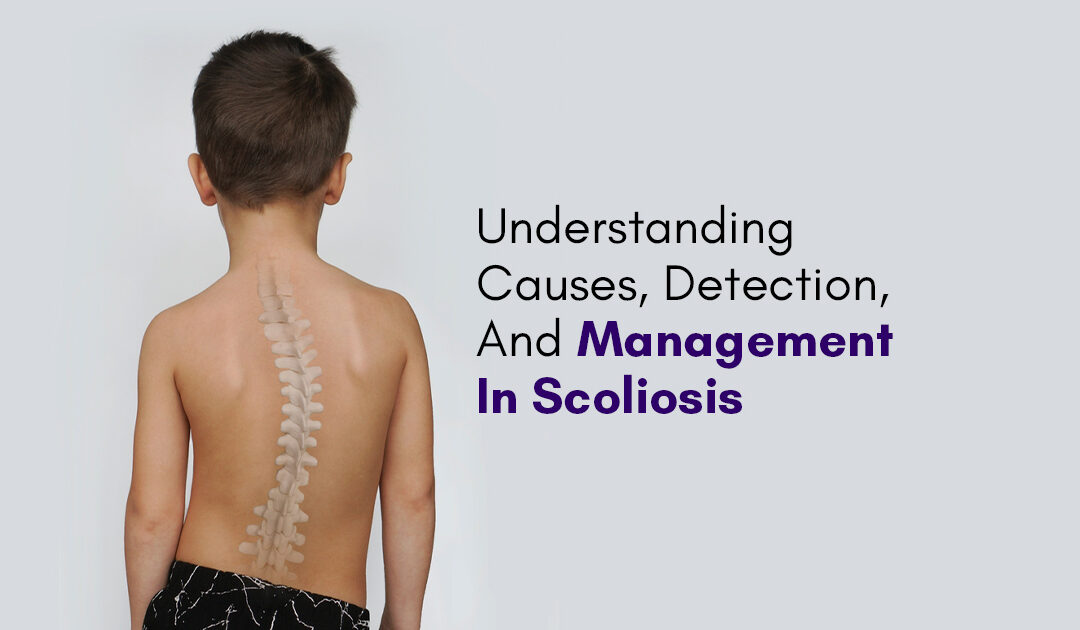
A sideways curvature of the spine, diagnosed mostly in young adults, is known as scoliosis. This is different from your body’s natural bending from front to back. While it’s generally mild and does not cause any symptoms, it may result in backache and abnormal posture. People with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy are more prone to developing scoliosis. However, the exact cause of most childhood scoliosis remains unknown.
The condition of scoliosis is usually mild but can worsen over time. It may even reach an intensity where it is disabling. In a serious scenario, a severe spinal curve may limit the amount of space within the chest, causing the lungs to experience difficulty in functioning properly. Children suffering from mild scoliosis are closely monitored with the help of X-rays to keep the curve from getting worse. In several cases, no treatment is recommended. Some children are asked to wear a brace to keep the curve straight. On the other hand, some may need surgery to straighten a more severe curve.
What Are the Symptoms of Scoliosis?
The symptoms of scoliosis may consist of
- Backache
- Inability or difficulty standing straight
- Weakness in core muscles
- Pain in the legs, accompanied by numbness or weakness
What Are the Signs of Scoliosis?
The signs of scoliosis are
- Uneven shoulders
- One shoulder blade that seems to stand out more than the other
- Uneven waist
- One hip elevated above the other
- One side of the rib cage protruding
- When leaning forward, there is a bulge on one side of the back
- Uneven leg length
- Loss of height
- Changes in skin appearance and texture, such as dimples, hair patches, and skin discoloration. These may appear on your back around your spine.
In addition to curving side to side, the majority of scoliosis cases involve the spine rotating or twisting. As a consequence, the ribs or muscles on one side of the body protrude more than those on the other.
What Part of the Spine Does Scoliosis Impact?
The condition of scoliosis can impact any region of your spine. However, they may be segregated based on age:
- In adolescents, scoliosis mostly occurs in the thoracic spine or rib cage region.
- In adults, the main problem occurs in the lumbar or lower spine region. The lumbar spine is more prone to changes seen with aging or degeneration, which elevates symptoms such as pain.
What Are the Causes of Scoliosis?
The cause of scoliosis may differ depending on the kind, but may consist of
- Vertebrae malformation at the time of embryonic development
- A change in the genetics
- An injury to the spine
- A spinal tumor
- A condition affecting your nerves or muscles
In most cases, healthcare professionals cannot identify a specific cause (idiopathic scoliosis).
What Are the Risk Factors of Scoliosis?
You’re more prone to developing scoliosis if you:
- Have a family history of scoliosis.
- Have an underlying condition or injury affecting your spine, muscles, and nerves.
Scoliosis does not discriminate between genders and sexes. However, women are more susceptible to needing treatment due to the severity of the curve. It is also important to note that not all cases of scoliosis are genetic.
How is Scoliosis Diagnosed?
The condition is usually diagnosed by a scoliosis screening where a healthcare provider may ask you to remove your shirt to see your back, stand straight, and bend forward to touch your toes. This is done to identify if there are any issues with the posture, alignment, and spinal curvature. Further, the healthcare provider may also recommend an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI if required. It is essential to get diagnosed with scoliosis early so you can manage your symptoms and achieve overall health faster.
If you notice the signs of scoliosis in yourself or your child, talk to your healthcare provider today.